Correlation Coefficient
Correlation coefficients are used
to measure how strong a relationship is between two variables. There are
several types of correlation coefficient, but the most popular is Pearson's
correlation. Pearson’s
correlation (also called Pearson’s R)
is a correlation coefficient commonly
used in linear regression. If you are starting out in statistics, you’ll
probably learn about Pearson’s R first.
In fact, when anyone refers to the correlation
coefficient, they are usually talking about Pearson’s.
Meaning
·
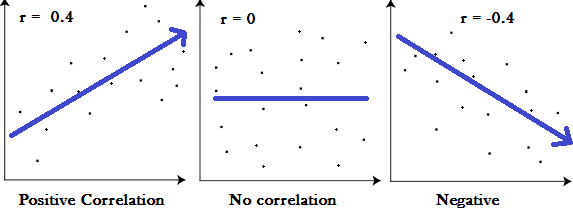
A correlation coefficient of 1 means that for every positive increase in
one variable, there is a positive increase of a fixed proportion in the other.
For example, shoe sizes go up in (almost) perfect correlation with foot length.
·
A correlation coefficient of -1 means that for every positive increase
in one variable, there is a negative decrease of a fixed proportion in the
other. For example, the amount of gas in a tank decreases in (almost) perfect
correlation with speed.
·
Zero means that for every increase, there isn’t a positive or negative
increase. The two just aren’t related.
Correlation coefficient formulas
are used to find how strong a relationship is between data. The formulas return
a value between -1 and 1, where:
·
1 indicates a strong positive relationship.
·
-1 indicates a strong negative relationship.

Comments
Post a Comment